ASP.Net Web
API is a lightweight framework using this, you can build stateless RESTful
services that run on HTTP/HTTPS.Exceptions are the errors that happen at
runtime. Exception handling is the technique to handle this runtime error in
our application code. If any error is thrown in web API that is caught, it is
translated into an HTTP response with status code 500- "Internal Server
Error".
These are
the ways to handle the exceptions in asp.net web api.
1.
HttpResponseException
2.
Exception Filters
3.
Exception Handler
4.
HttpError
Here i am
using student class for example first i create student model , you can copy and
paste in IDE for practicle.
public class
StudentModel
{
public int
Id { get;
set; }
public string Email { get; set;
}
public string Name { get; set;
}
}
For data i
am using method which return list but you can get from database also for real time.
public class StudentRepository
{
public List<StudentModel> GetList()
{
return new
List<StudentModel>
{
new StudentModel {Id=1,Name="ABC",Email="ABC@gmail.com" },
new StudentModel {Id=2,Name="XYZ",Email="xyz@gmail.com" },
new StudentModel {Id=3,Name="RAM",Email="ram@gmail.com" }
};
}
}
Using HttpResponseException
This
exception returns any HTTP status code from your controller methods that you
specify in the exception constructor. For example, the following method returns
404, Not Found, if the id parameter is not valid.
public class
StudentController : ApiController
{
//
return only status code in Exception
public HttpResponseMessage Get(int id)
{
StudentRepository repository = new StudentRepository();
var studentDetail = repository.GetList().Where(x => x.Id ==
id).FirstOrDefault();
if (studentDetail == null)
{
//use
of HttpReponseException class
//in
constructor we can pass any type of status
throw new
HttpResponseException(HttpStatusCode.NotFound);
}
return Request.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.OK, studentDetail);
}
You can also
return any user define message along with status code , following example
return status code with user define message.
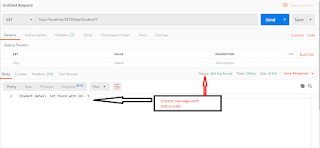
public HttpResponseMessage GetStudent(int id)
{
StudentRepository repository = new StudentRepository();
var studentDetail = repository.GetList().Where(x => x.Id ==
id).FirstOrDefault();
if (studentDetail == null)
{
//use
of HttpReponseException class
//in
constructor we can pass any type of status
var response = new HttpResponseMessage(HttpStatusCode.NotFound)
{
//user define message
Content = new StringContent(
string.Format("Student detail not
found with id:- {0}", id)
),
StatusCode = HttpStatusCode.NotFound
};
throw new
HttpResponseException(response);
}
return Request.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.OK, studentDetail);
Using Exception Filters
The
exception filter can be able to catch the unhandled exceptions in Web API. This
filter is executed when an action method throws the unhandled exception. Note
that exception filter does not catch HttpResponseException
exception because HttpResponseException is specifically designed to return the
HTTP response.
To create an
exception filter, you need to implement the IExceptionFilter interface. You can also create exception filters
by extending the abstract class ExceptionFilterAttribute
and then overriding the OnException
method.
Note that the
ExceptionFilterAttribute abstract class in turn implements the IExceptionFilter
interface.
The
following code snippet illustrates how you can create a custom exception filter
by extending the ExceptionFilterAttribute class and then overriding the
OnException method
//Create
class and inherit from ExceptionFilterAttribute class
public class
CustomExceptionAttribute : ExceptionFilterAttribute
{
public override void
OnException(HttpActionExecutedContext actionExecutedContext)
{
actionExecutedContext.Response =
actionExecutedContext.Request
.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.InternalServerError,
"Some exception occure..please try later.");
base.OnException(actionExecutedContext);
}
}
You should
add the custom exception filter to the filters collection of the
HttpConfiguration object.
public static class
WebApiConfig
{
public static void
Register(HttpConfiguration config)
{
//
Web API configuration and services
//
Configure Web API to use only bearer token authentication.
config.SuppressDefaultHostAuthentication();
config.Filters.Add(new HostAuthenticationFilter(OAuthDefaults.AuthenticationType));
config.Filters.Add(new CustomExceptionAttribute());
config.Formatters.Remove(config.Formatters.JsonFormatter);
//
Web API routes
config.MapHttpAttributeRoutes();
config.Routes.MapHttpRoute(
name: "DefaultApi",
routeTemplate: "api/{controller}/{id}",
defaults: new { id = RouteParameter.Optional }
);
}
}
You can
register your exception filters in one of the following three ways:
1. At
the action level
2. At
the controller level
3. Globally
At Action Level
To apply the
filter to a specific action, add the filter as an attribute to the action:
public class
StudentController : ApiController
{
//
Excetion Filter Attribute
[CustomExceptionAttribure]
public HttpResponseMessage Get(int id)
{
StudentRepository repository = new StudentRepository();
var studentDetail = repository.GetList().Where(x => x.Id ==
id).FirstOrDefault();
return Request.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.OK, studentDetail);
}
}
At the controller level.
To apply the filter to all of the
actions on a controller, add the filter as an attribute to the controller
class:
//
Excetion Filter Attribute at controller level
[CustomExceptionAttribure]
public class
StudentController : ApiController
{
//code here--
}
Globally
To
apply the filter globally to all Web API controllers, add an instance of the
filter to the GlobalConfiguration.Configuration.Filters
collection. Exception filters in this collection apply to any Web API
controller action.
GlobalConfiguration.Configuration.Filters.Add(new CustomExceptionAttribure());
If you use the "ASP.NET MVC 4 Web
Application" project template to create your project, put your Web API
configuration code inside the WebApiConfig class, which is located in the
App_Start folder:
public static class
WebApiConfig
{
public static void
Register(HttpConfiguration config)
{
//
Web API configuration and services
config.SuppressDefaultHostAuthentication();
config.Filters.Add(new HostAuthenticationFilter(OAuthDefaults.AuthenticationType));
config.Filters.Add(new CustomExceptionAttribute());
}
}
Using Exception Handlers
Normally,
exception filter is used to catch the unhandled exception. This approach will
work fine but it fails if any error is raised from outside action. For example,
if any error is raised in the following area then exception filter will not
work.
• Error inside the exception filter.
• Exception related to routing.
• Error inside the Message Handlers
class.
• Error in Controller Constructor.
Web API 2
provides a good alternative way to achieve global exception handling. Web API
provides "ExceptionHandler"
abstract class to handle exception.
public class
GlobalExceptionHandler
: ExceptionHandler
{
public override Task HandleAsync(ExceptionHandlerContext context, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
const string errorMessage = "An unexpected
error occured";
var response = context.Request.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.InternalServerError,
new
{
Message = errorMessage
});
response.Headers.Add("X-Error",
errorMessage);
context.Result = new ResponseMessageResult(response);
return base.HandleAsync(context,
cancellationToken);
}
}
Same as
exception filter, Exception handler is also required to be registered.
ExceptionHandler is inheriting from IExceptionHandler interface and Web API has
already this type of class registered so we just need to replace this class to
our custom exception handler class because Web API doesn’t support multiple
ExceptionHandler.
config.Services.Replace(typeof(IExceptionHandler), new GlobalExceptionHandler());
Using HttpError
The HttpError
object provides a consistent way to return error information in the response
body. The following example shows how to return HTTP status code 404 (Not
Found) with an HttpError in the response body.
//for
http error attribute
public HttpResponseMessage GetStudent1(int id)
{
StudentRepository repository = new StudentRepository();
var studentDetail = repository.GetList().Where(x => x.Id ==
id).FirstOrDefault();
if (studentDetail == null)
{
string _message = string.Format("Student
detail not found with id:- {0}", id);
return Request.CreateErrorResponse(HttpStatusCode.NotFound, _message);
}
return Request.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.OK, studentDetail);
}
CreateErrorResponse is an extension method defined in
the System.Net.Http.HttpRequestMessageExtensions
class. Internally, CreateErrorResponse
creates an HttpError instance and then creates an HttpResponseMessage that
contains the HttpError.
Notice that the HttpError was
serialized to JSON in this example. One advantage of using HttpError is that it
goes through the same content-negotiation and serialization process as any
other strongly-typed model.

No comments:
Post a Comment